(noun. /pruh-MOW-tr)
by Leslie Kent
What does it mean?
A promoter is a short region of DNA where proteins such as RNA polymerase bind so that they can transcribe DNA. RNA polymerase is an enzyme, or type of protein, that reads our DNA and makes an RNA copy. This RNA then goes on to do other jobs in the cell, such as making proteins, to keep organisms (like us!) alive and able to grow. Promoters help RNA polymerase recognize where to start making RNA. Other proteins, called transcription factors, can also bind to DNA and change how easy it is for RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter.
How do I use it in a sentence?
“Our cells use promoters to ‘promote’ DNA transcription.”
“The repressor protein bound to the DNA prevented RNA polymerase from binding to the promoter and transcribing the gene.”
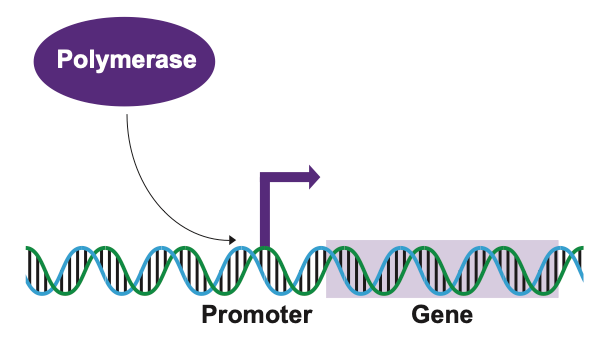
RNA polymerase (pictured here as a purple oval) binds to a promoter (pictured here as a purple arrow pointing toward a gene) in the genome to know where to start transcribing DNA. Image created by Leslie Kent using Adobe Illustrator.
