Noun. /DIF-uh-ren-shee-AY-shun/
by Jessica Zhang
What does it mean?
Differentiation is the process by which an unspecialized cell – such as a stem cell – develops into a specific type of cell with distinct functions, such as a muscle cell, brain cell, or blood cell.
You can think of differentiation as a cell’s life journey. At key points during development, cells must “make decisions” about what type they’ll become. This idea is famously illustrated by the Waddington landscape model.
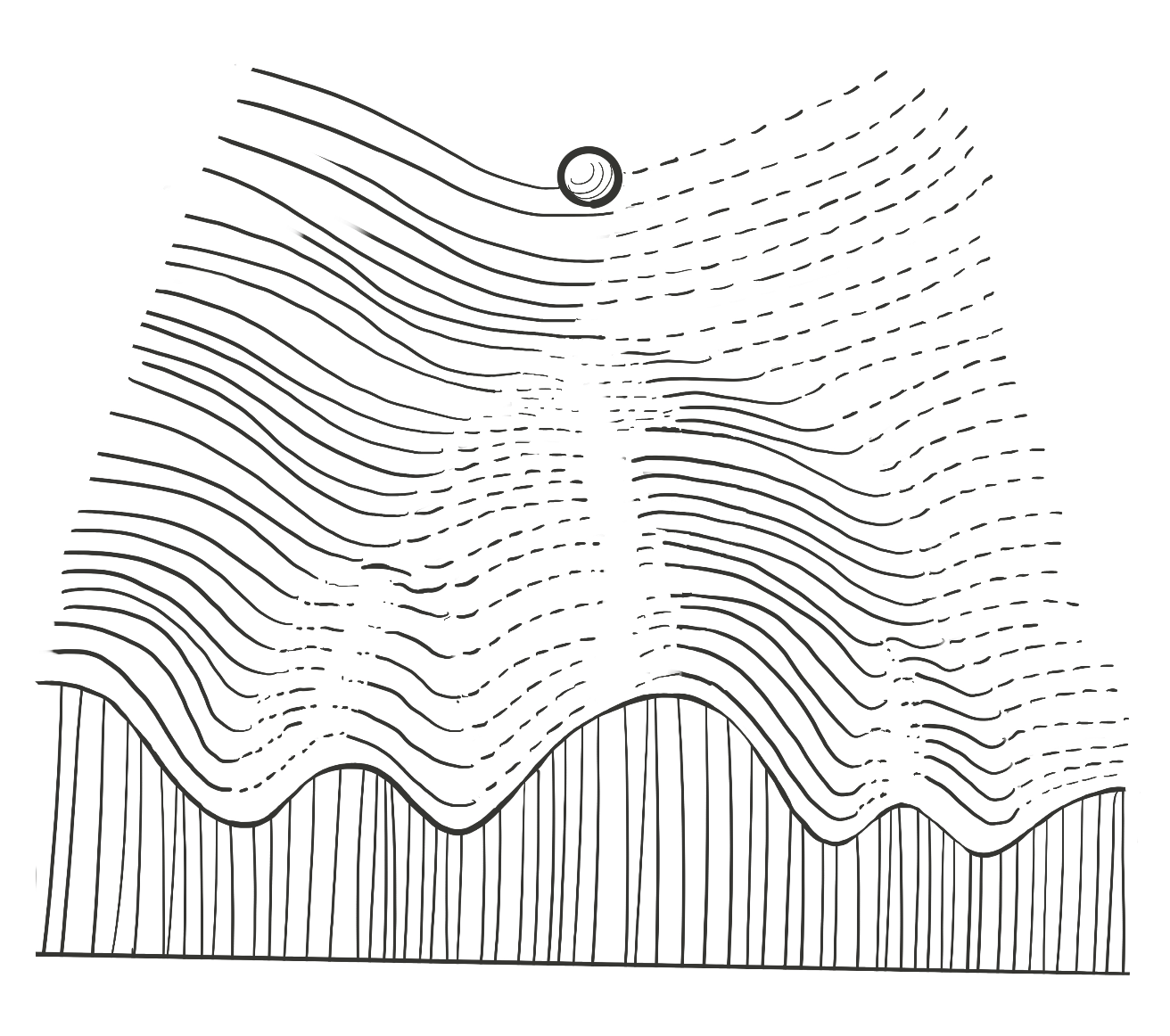
Figure 1: The Waddington landscape, introduced by scientist C.H. Waddington in 1957, is a way to show how stem cells develop into different types of cells. Imagine a ball rolling down a hill—at the top, the ball can go in many directions. Each path or valley the ball rolls into represents a different kind of cell. Once it reaches the bottom, it’s hard to go back. But scientists have now found ways to push the cell back up the hill and change it into a different type again, reversing its fate.
Image adapted from image source
How do I use it in a sentence?
Thanks to differentiation, a single fertilized egg can eventually develop into a whole organism with many different cell types.
Etymology
From the Latin word “differō”, meaning “to separate”.
Related terms
Stem cell
Potency
Induced pluripotent stem cell
Cell fate specification
Lineage
Developmental trajectory
Gene expression
Epigenetics
Fields of study in which this word is commonly used
Developmental biology
Cell and molecular biology
Regenerative medicine
Cancer biology
