by Brianna Almeida
Fun Rating: 2/5

Difficulty Rating: 3/5
What is the general purpose?
The purpose of gel electrophoresis is to determine whether a sample of interest contains DNA fragments and estimate their size.
Why do we use it?
We often use gel electrophoresis after performing DNA extractions to confirm the presence of DNA in a sample. We also use this technique after PCRs (polymerase chain reactions) to ensure that the targeted DNA fragment was successfully amplified.
How does it work?
First, you need to make the gel! The gel is made from a buffer and agarose which, when melted and then cooled, solidifies into a jelly-like substance. In addition to buffer and agar, a DNA binding stain is added to the solution before it solidifies, so that the DNA can be visualized.
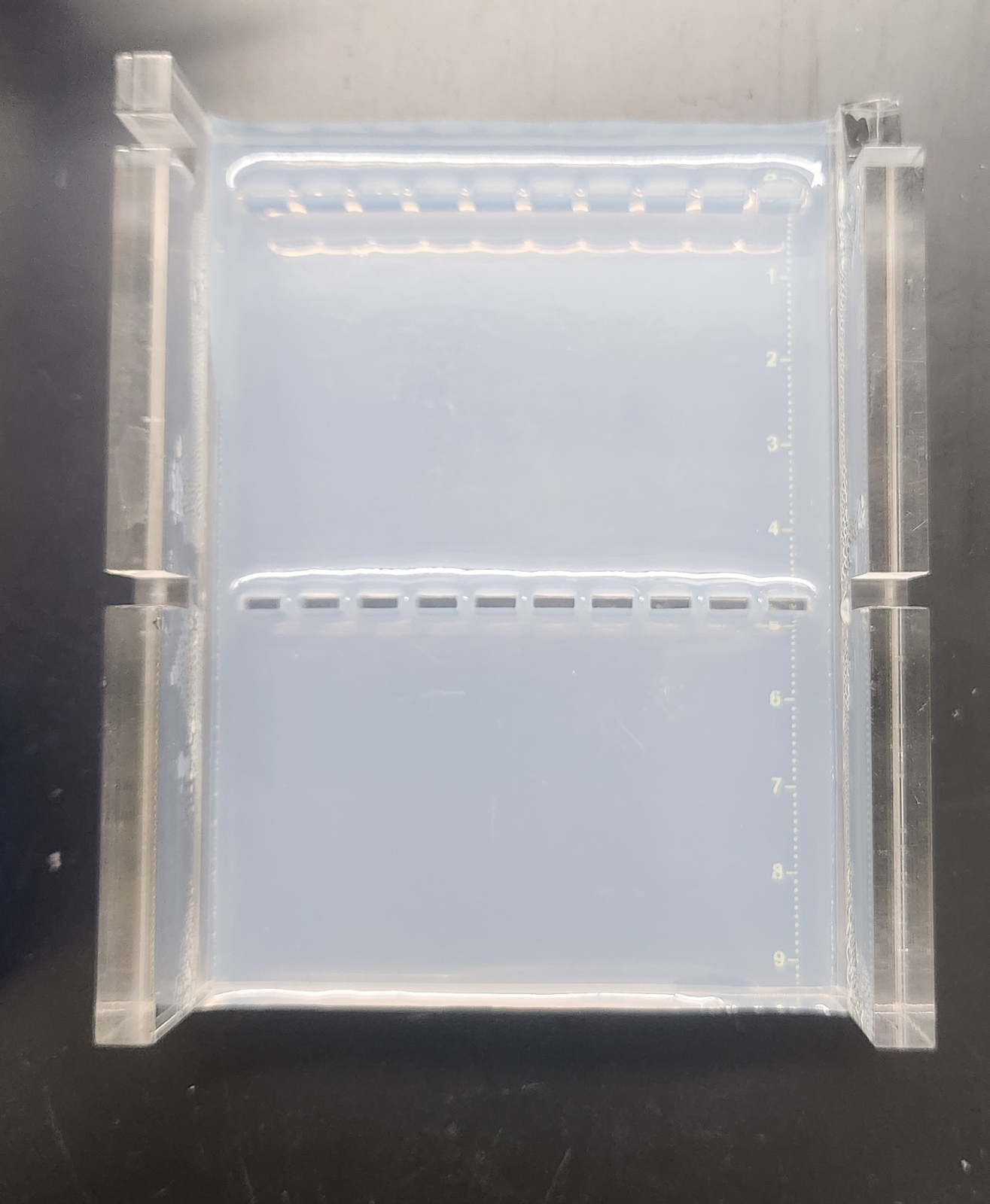
Solidified agarose gel. Image taken by Brianna Almeida.
Then, the gel is placed in a salty buffer solution and a small amount of DNA sample is loaded carefully into the wells at the top of the gel using a pipette. In addition to DNA samples, a DNA ladder is loaded into one of the wells. This ladder contains fragments of DNA at different sizes that can be compared to your DNA samples of interest to estimate their size.
An electric current is passed through the buffer solution so that the top of the gel is negatively charged, and the bottom of the gel is positively charged. DNA is negatively charged, making it attracted to the positive charge at the bottom of the gel, and the current pushes the DNA down the gel. The gel acts as a filter with tiny pores that will only allow certain DNA fragment sizes through. Larger fragments are stuck at the top and smaller fragments move further down the gel.
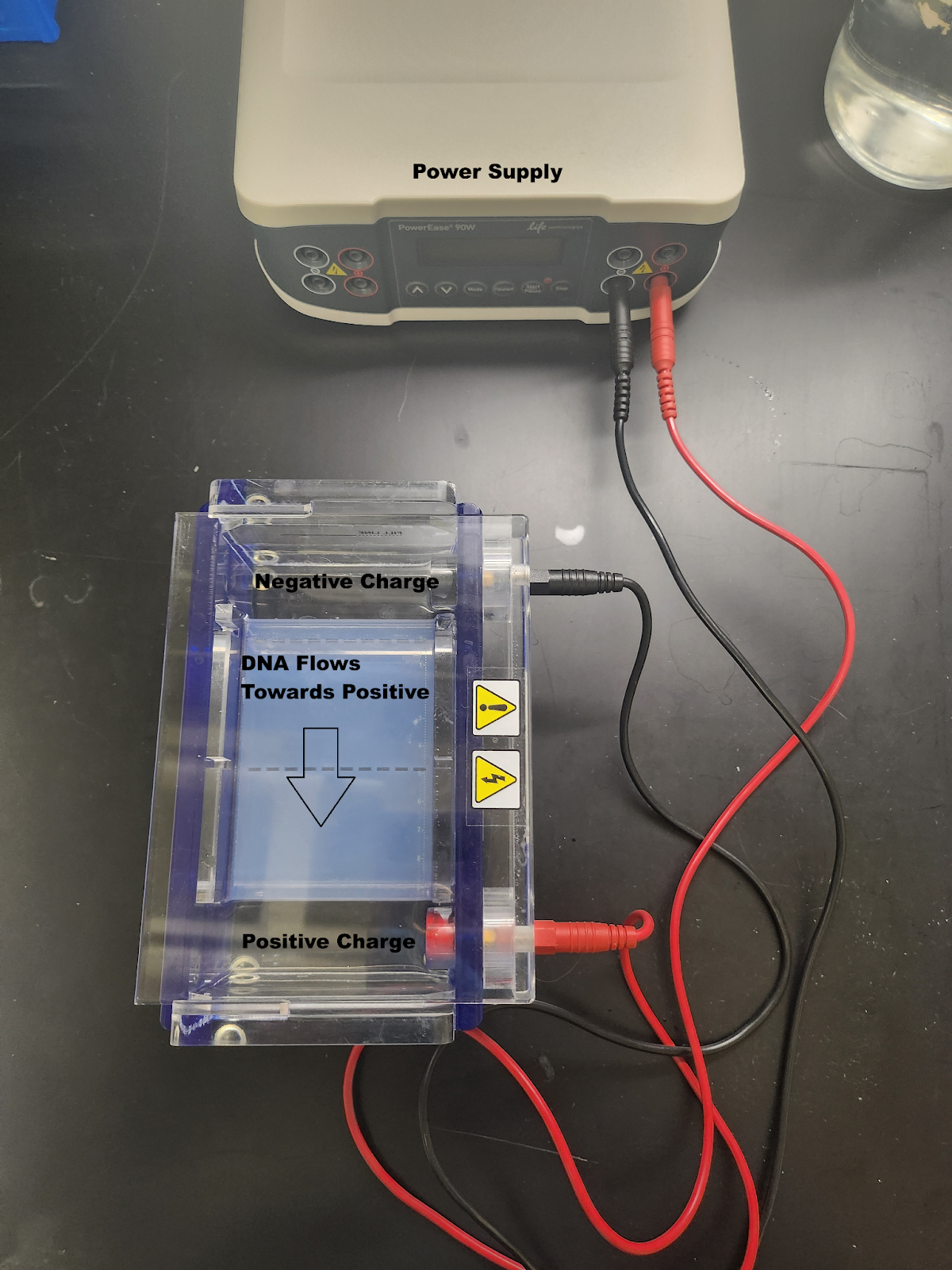
Image of gel electrophoresis set up, attached to power supply. Image taken and modified by Brianna Almeida
Finally, you need to image the gel to see the DNA bands of your samples and compare the DNA fragments to the ladder to determine the size of the fragments. The DNA binding stain can be seen if placed under blue or UV light. If the stain needs UV light, goggles or a special transparent plastic layer are used to protect the eyes. Then you can take an image of the gel and put it in your lab notebook.
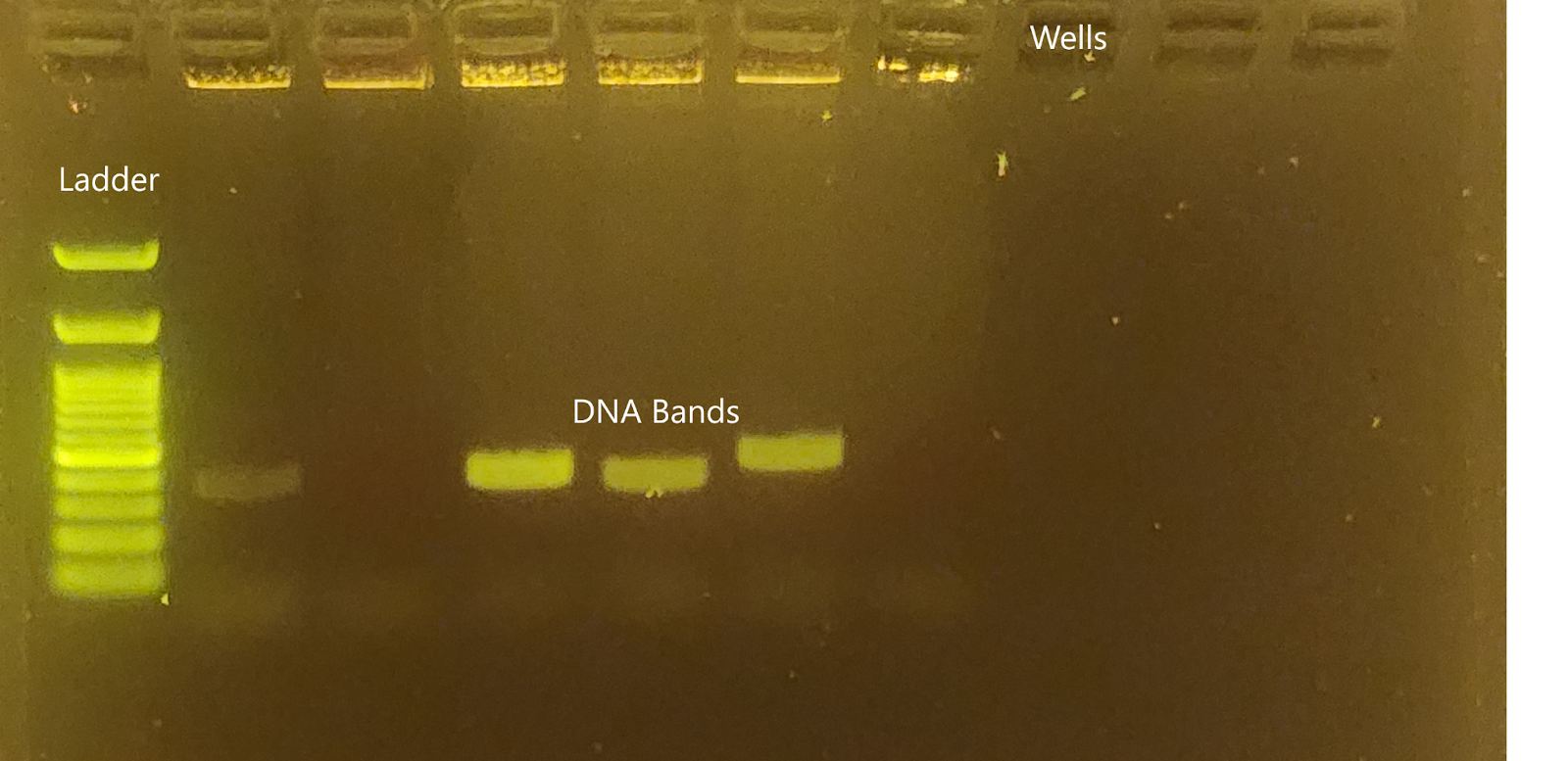
Image of a gel containing a DNA ladder and DNA samples, taken and modified by Brianna Almeida
