by Marco Gontijo
What does it mean?
Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria and other microorganisms develop the ability to survive antibiotics—the medicines meant to kill or stop them from growing. Instead of dying off, these bacteria multiply, making infections more challenging to treat. Based on their susceptibility to antibiotic treatment, bacteria can be classified into (Figure 1):
- Drug-Susceptible (DS) bacteria: bacteria killed or stopped by at least one drug in each relevant antibiotic class.
- Drug-Resistant (DR) bacteria: bacteria are no longer affected by at least one antibiotic that would usually kill or stop their growth.
- Multidrug-Resistant (MDR) bacteria: bacteria resistant to at least one antibiotic in three or more different classes of antibiotics.
- Extensively Drug-Resistant (XDR) bacteria: bacteria resistant to almost all available antibiotics.
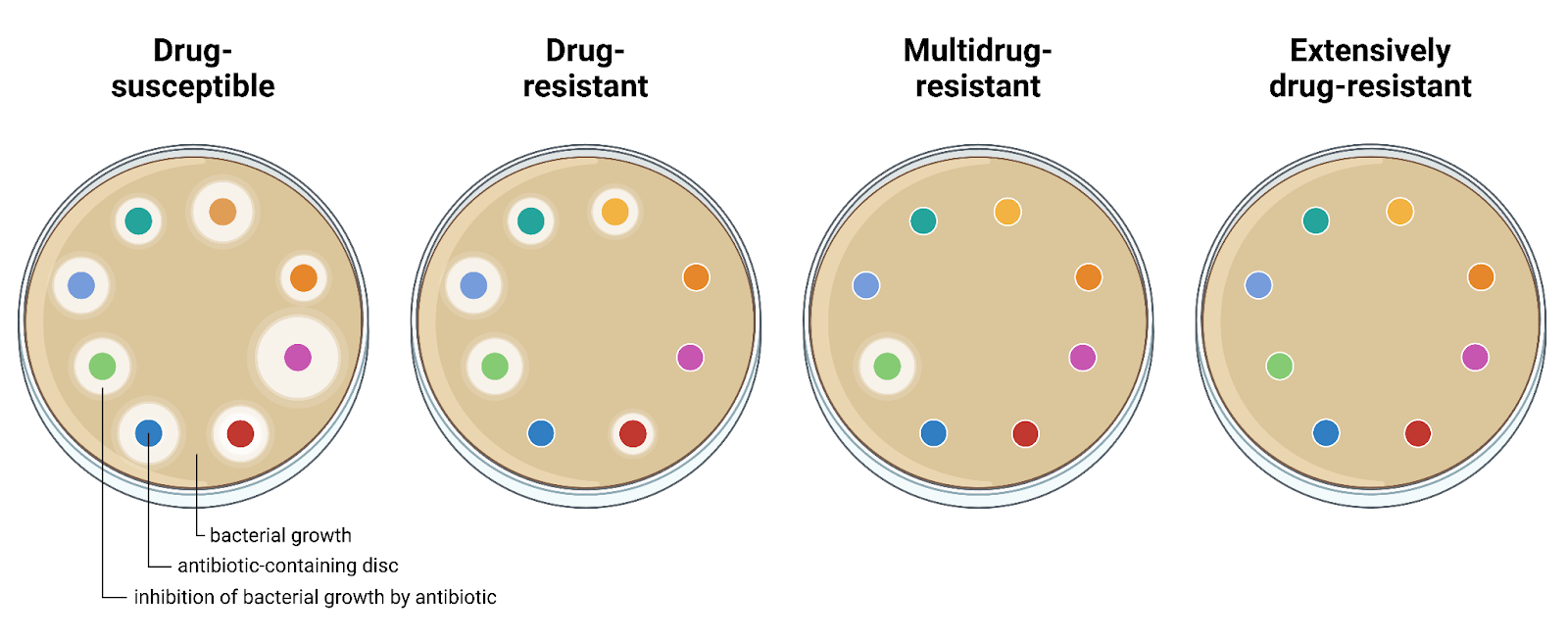
Figure 1. Illustration of bacterial responses to antibiotics using the disc diffusion method. In this assay, antibiotic-impregnated discs are placed on an agar plate seeded with bacteria. The antibiotic diffuses outward from each disc, and if effective, creates a clear zone (halo) of inhibited bacterial growth. Resistance increases from left to right: the plate on the far left shows a drug-susceptible strain inhibited by all antibiotics (visible halos around every disc), while the far-right plate represents an extensively drug-resistant strain, where no antibiotics successfully impede growth. As resistance increases from left to right, fewer antibiotic discs can inhibit bacterial growth, shown by the absence of clear zones around the discs. Figure created by author in BioRender.
How do I use it in a sentence?
“The doctor said the infection didn’t respond to treatment because the bacteria had developed antibiotic resistance.”
Etymology
Antibiotic: from Greek anti- (“against”) + bios (“life”)
Resistance: from Latin resistentia (“opposition, resistance”)
Put together, it means “opposing life-stopping agents”—and that’s precisely what resistant bacteria do.
Related terms
Plasmid, Horizontal Gene Transfer, Superbug
Fields of study in which this word is commonly used
Microbiology, Public Health, Infectious Disease Medicine, Genetics
