(Noun. / di-FYOO-zhun)
by Doris Cruz Alonso
What does it mean?
Diffusion is the net passive movement of molecules (liquid, solid, or gas) from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration. Diffusion is a fundamental concept in physics, chemistry, and biology, and it plays a crucial role in all living beings. It helps the movement of substances in and out of the cells. For diffusion to occur, there needs to be a concentration gradient which refers to the gradual change in the concentrations of substances within the regions of interest. The difference in concentrations is what causes the molecules to diffuse between the two regions. An example of when diffusion occurs in a biological system is the transfer of oxygen and carbon dioxide across the lung’s membrane.
How do I use it in a sentence?
The smell of a rotten egg in the kitchen gradually spread throughout the entire dining room due to diffusion, creating an unpleasant odor in the entire area.
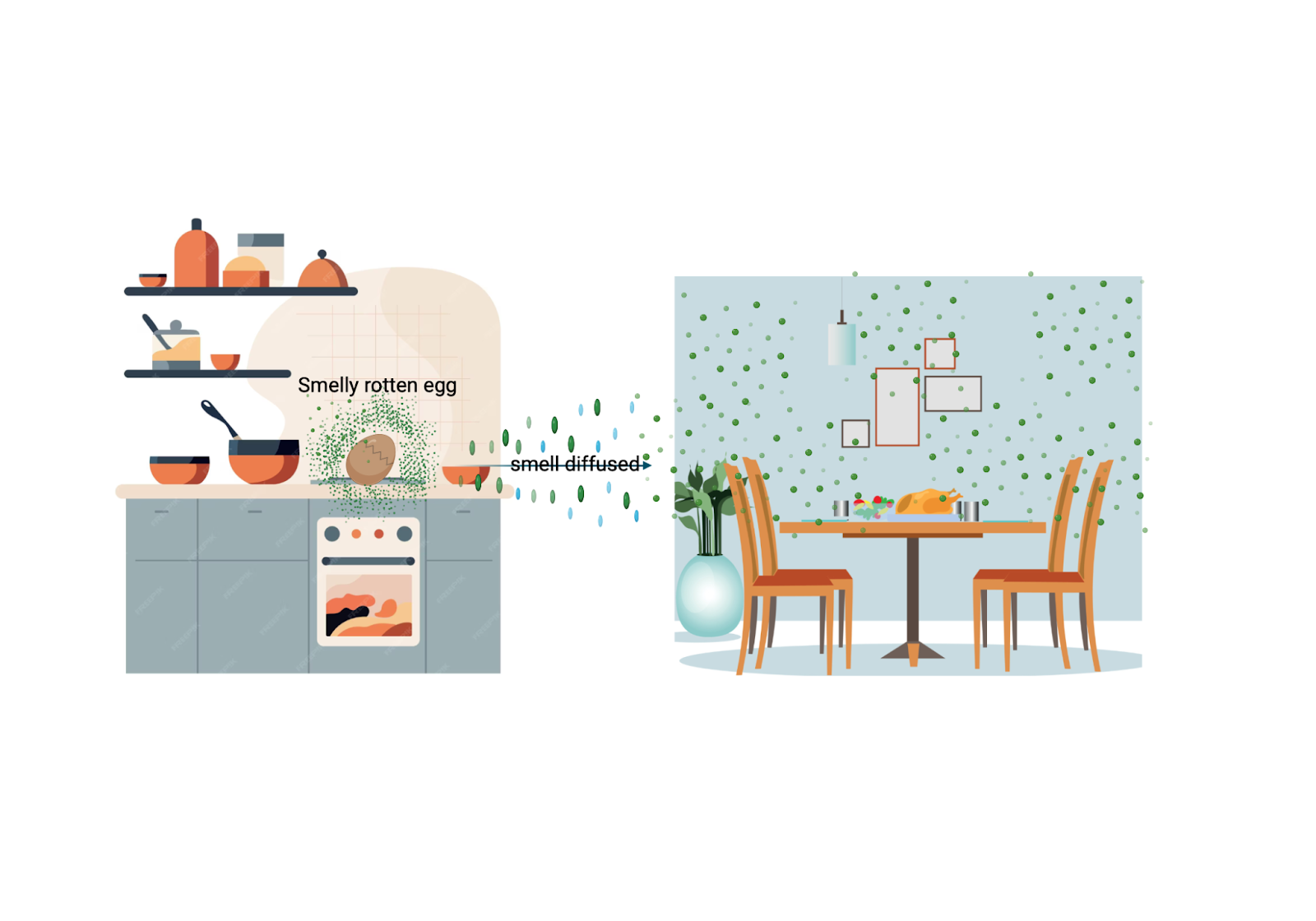
Example of diffusion. Image created in BioRender by Doris Cruz Alonso
Related terms
Osmosis
Rate of flow
Active transport
