by Marco Gontijo
What does it mean?
Phagocyte is a type of immune cell that engulfs and digests harmful microorganisms, dead cells, and debris, playing a crucial role in immune defense and tissue maintenance.
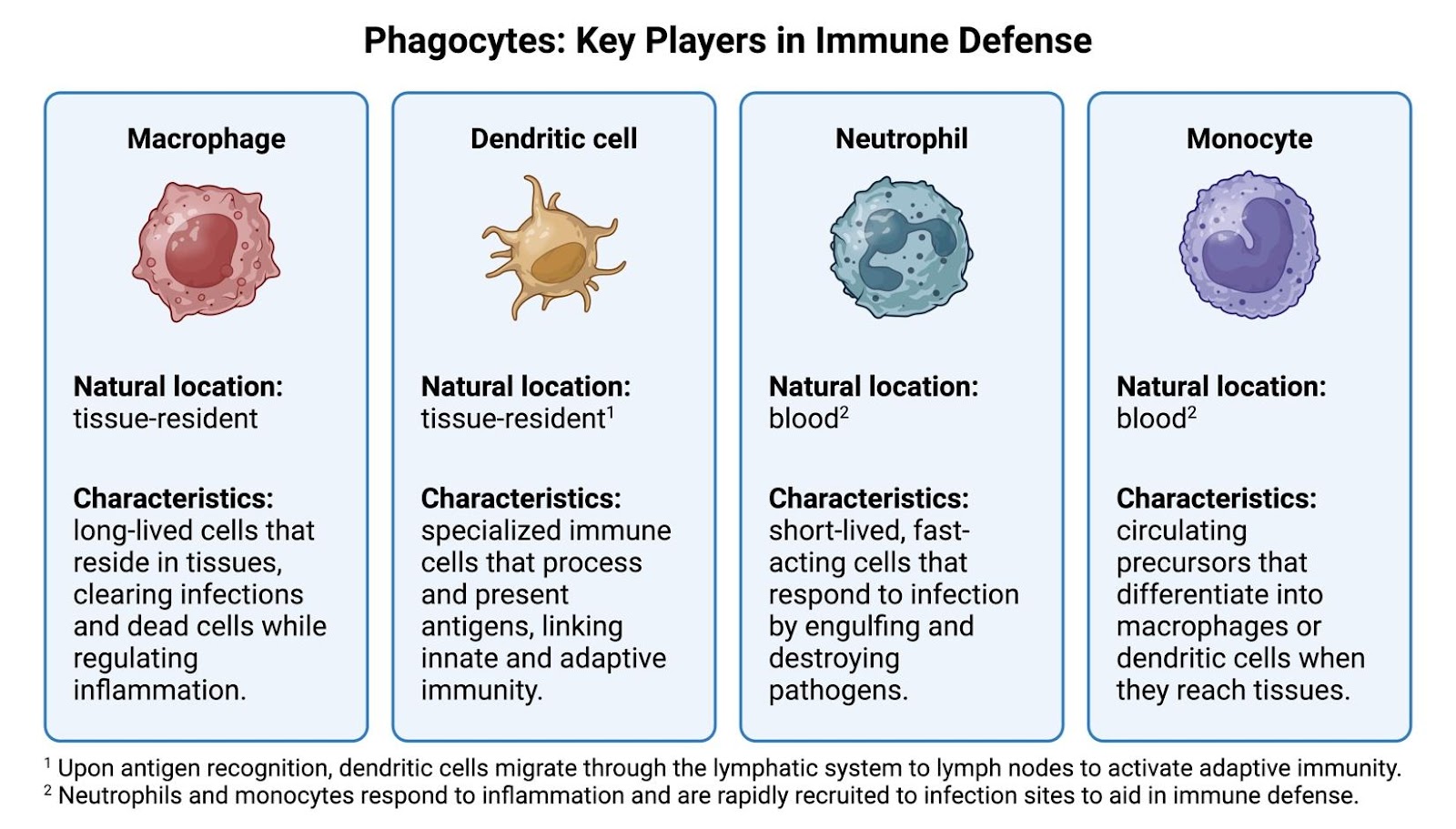
Figure 1: Types of immune cells and their functions, created by author in BioRender. Lab, S. (2025).
Phagocytes are immune cells that engulf and eliminate pathogens, playing a crucial role in both innate and adaptive immunity. This figure highlights four major types: macrophages, dendritic cells, neutrophils, and monocytes. Their natural locations and specialized functions contribute to immune homeostasis and pathogen clearance.
How do I use it in a sentence?
“Macrophages are phagocytes that help eliminate bacteria by engulfing them through phagocytosis.”
Etymology
From Greek phagein (“to eat”) + cyte (“cell”), meaning “eating cell.”
Related Terms
Hematopoiesis, Antibody, Enzyme, Flagella, Macrocytes, Red Blood Cells.
Fields of Study
Immunology, Microbiology, Cell Biology, Pathology, Hematology.
