(noun. /floor-ESS-uns/)
By Rami Major
What does it mean?
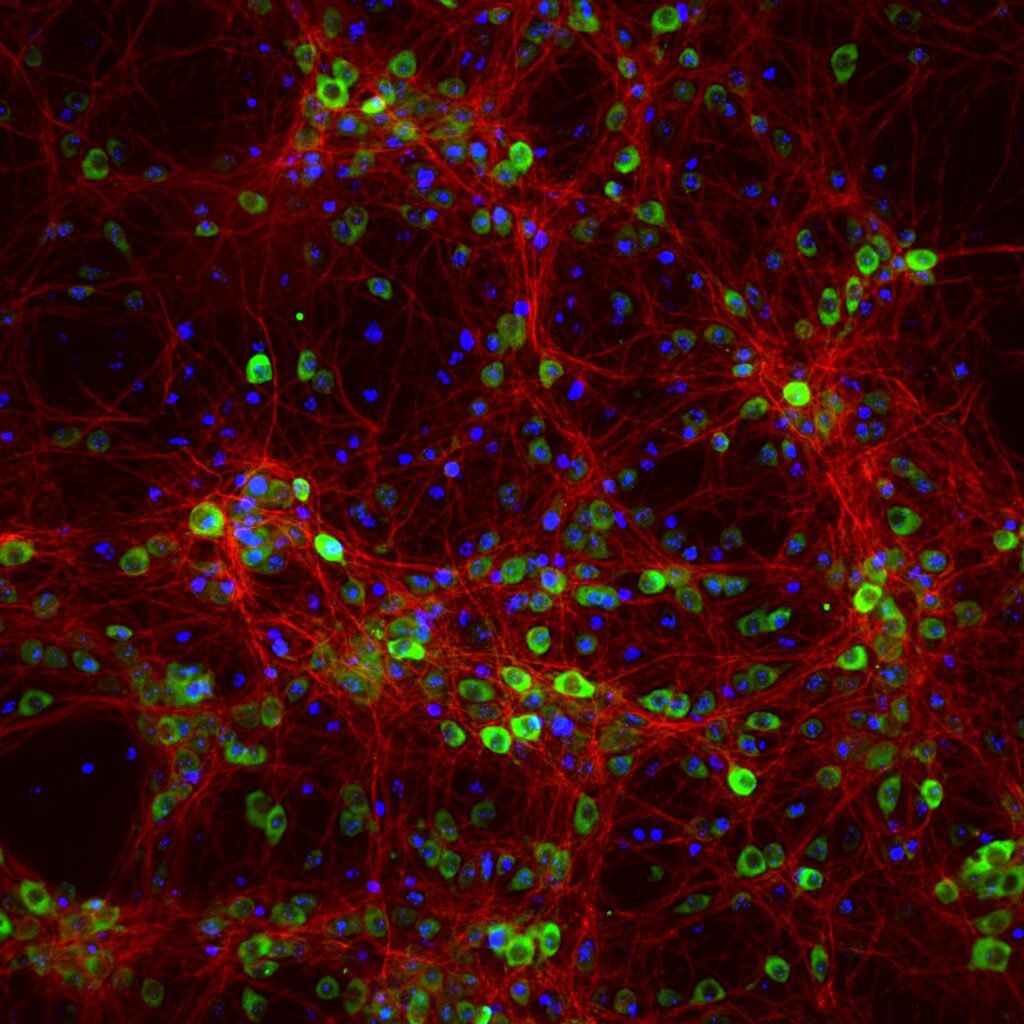
Light travels in waves. The length of these waves (also called the wavelength) varies and changes the characteristics of the light. Light with shorter wavelengths carries more energy, while light with longer wavelengths carries less energy. Fluorescence occurs when a substance absorbs light with shorter wavelengths and emits it in the form of light with longer wavelengths. The result: the substance itself seems to glow!
How do I use it in a sentence?
“Scientists use a microscope with special detectors to observe the fluorescence of cells that contain a green fluorescent protein.”